History
Von Neumann Machine
Utilises the stored program concept - First published in 1945 by John von Neumann
Completed in 1952, the IAS computer is the prototype for all subsequent general-purpose computers
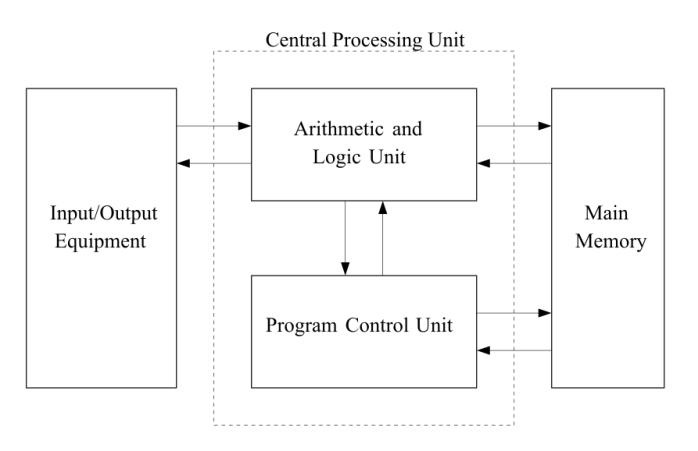
Structure
- Main memory - for storing programs alongside data
- An Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) - capable of operating on binary data
- A Control Unit - interprets instruction in memory and executes them
- Input and Output - operated by the control unit
Design
The Bus
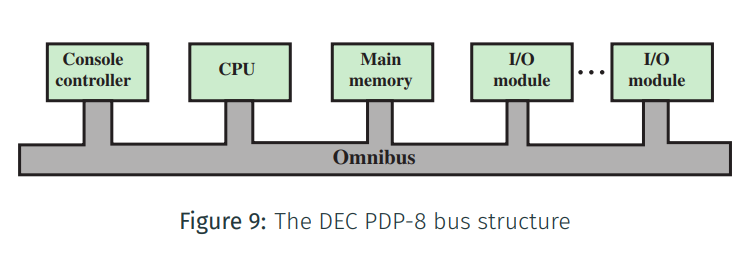
DEC PDP-8
1964
The DEC PDP-8 was the first minicomputer
- Didn't require an air-conditioned room
- Could sit on a lab bench / desk
- Cost only ~$16,000
The DEC was the first commercial device to use a bus structure instead of switches
The Structure
Gordon Moore's Law
1965: Every year the number of transistors on a chip would double every year
1975: Every other year the number of...In reality, it has been every 18 months
- The cost of a chip has remained relatively stable throughout the years
- Higher packing density means shorter electrical paths, giving higher performance
- Smaller size gives increased flexibility
- Power and cooling requirements are reduced
- Fewer interconnections reduces points of failure - improving reliability
Performance
- Processor speed is increasing
- Memory Capacity is increasing
- Memory speed lags behind processor speed
Performance Measures
- Various measures are used to assess performance - e.g. memory bandwidth, MIPS. MFLOPS
- The maximum possible will be the value advertised
- Speed often competes with size (or memory) and both must be balanced against cost
- Software availability, ease of maintenance, etc. are also important